Dynamik: Kraftgesetze 20
About points...
We associate a certain number of points with each exercise.
When you click an exercise into a collection, this number will be taken as points for the exercise, kind of "by default".
But once the exercise is on the collection, you can edit the number of points for the exercise in the collection independently, without any effect on "points by default" as represented by the number here.
That being said... How many "default points" should you associate with an exercise upon creation?
As with difficulty, there is no straight forward and generally accepted way.
But as a guideline, we tend to give as many points by default as there are mathematical steps to do in the exercise.
Again, very vague... But the number should kind of represent the "work" required.
When you click an exercise into a collection, this number will be taken as points for the exercise, kind of "by default".
But once the exercise is on the collection, you can edit the number of points for the exercise in the collection independently, without any effect on "points by default" as represented by the number here.
That being said... How many "default points" should you associate with an exercise upon creation?
As with difficulty, there is no straight forward and generally accepted way.
But as a guideline, we tend to give as many points by default as there are mathematical steps to do in the exercise.
Again, very vague... But the number should kind of represent the "work" required.
About difficulty...
We associate a certain difficulty with each exercise.
When you click an exercise into a collection, this number will be taken as difficulty for the exercise, kind of "by default".
But once the exercise is on the collection, you can edit its difficulty in the collection independently, without any effect on the "difficulty by default" here.
Why we use chess pieces? Well... we like chess, we like playing around with \(\LaTeX\)-fonts, we wanted symbols that need less space than six stars in a table-column... But in your layouts, you are of course free to indicate the difficulty of the exercise the way you want.
That being said... How "difficult" is an exercise? It depends on many factors, like what was being taught etc.
In physics exercises, we try to follow this pattern:
Level 1 - One formula (one you would find in a reference book) is enough to solve the exercise. Example exercise
Level 2 - Two formulas are needed, it's possible to compute an "in-between" solution, i.e. no algebraic equation needed. Example exercise
Level 3 - "Chain-computations" like on level 2, but 3+ calculations. Still, no equations, i.e. you are not forced to solve it in an algebraic manner. Example exercise
Level 4 - Exercise needs to be solved by algebraic equations, not possible to calculate numerical "in-between" results. Example exercise
Level 5 -
Level 6 -
When you click an exercise into a collection, this number will be taken as difficulty for the exercise, kind of "by default".
But once the exercise is on the collection, you can edit its difficulty in the collection independently, without any effect on the "difficulty by default" here.
Why we use chess pieces? Well... we like chess, we like playing around with \(\LaTeX\)-fonts, we wanted symbols that need less space than six stars in a table-column... But in your layouts, you are of course free to indicate the difficulty of the exercise the way you want.
That being said... How "difficult" is an exercise? It depends on many factors, like what was being taught etc.
In physics exercises, we try to follow this pattern:
Level 1 - One formula (one you would find in a reference book) is enough to solve the exercise. Example exercise
Level 2 - Two formulas are needed, it's possible to compute an "in-between" solution, i.e. no algebraic equation needed. Example exercise
Level 3 - "Chain-computations" like on level 2, but 3+ calculations. Still, no equations, i.e. you are not forced to solve it in an algebraic manner. Example exercise
Level 4 - Exercise needs to be solved by algebraic equations, not possible to calculate numerical "in-between" results. Example exercise
Level 5 -
Level 6 -
Question
Solution
Short
Video
\(\LaTeX\)
Need help? Yes, please!
The following quantities appear in the problem:
Federkonstante \(D\) /
The following formulas must be used to solve the exercise:
\(D = D_1 + D_2 \quad \) \(\frac{1}{D} = \frac{1}{D_1} + \frac{1}{D_2} \quad \)

No explanation / solution video to this exercise has yet been created.
Visit our YouTube-Channel to see solutions to other exercises.
Don't forget to subscribe to our channel, like the videos and leave comments!
Visit our YouTube-Channel to see solutions to other exercises.
Don't forget to subscribe to our channel, like the videos and leave comments!
Exercise:
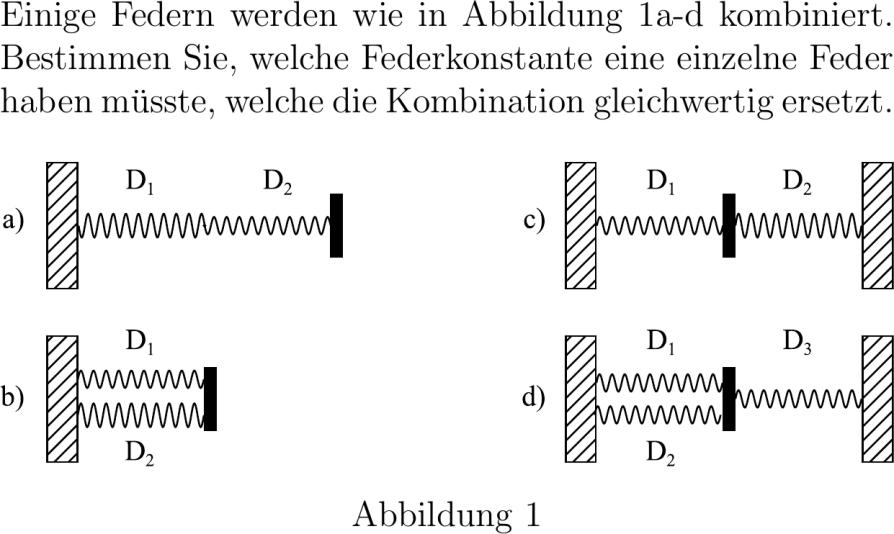
Einige Federn werden wie in Abbildung reffig:FedernKombinationena-d kombiniert. Bestimmen Sie welche Federkonstante eine einzelne Feder haben müsste welche die Kombination gleichwertig ersetzt. figureH includegraphicswidthtextwidth#image_path:FedernKombinationen# caption labelfig:FedernKombinationen figure
Solution:
% . September Lie. * &textFedergesetz: F_ D_ x_ quad F_ D_ x_ quad F_res D_res x_res &texta Die Spannkraft ist überall gleich F aber die Dehnungen x_i sind verschieden: &quad x_res x_ + x_Rightarrow fracFD_res fracFD_+fracFD_ Rightarrow fracD_res fracD_ + fracD_ Rightarrow D_res fracD_D_D_+D_ &textb Die Dehnungen sind gleich x aber die Spannkräfte F_i sind verschieden: &quad F_res F_ + F_Rightarrow D_resx D_x+D_x Rightarrow D_res D_+D_ &textc Dehnungen: x_res x_-x_ Spannkräfte: verschieden und entgegengesetzt gerichtet: &quad F_res F_ - F_Rightarrow D_resx D_x-D_-x Rightarrow D_res D_+D_ &textd Das ist eine Kombination von b und c also ist &quad D_res D_+D_+D_ * newpage
Einige Federn werden wie in Abbildung reffig:FedernKombinationena-d kombiniert. Bestimmen Sie welche Federkonstante eine einzelne Feder haben müsste welche die Kombination gleichwertig ersetzt. figureH includegraphicswidthtextwidth#image_path:FedernKombinationen# caption labelfig:FedernKombinationen figure
Solution:
% . September Lie. * &textFedergesetz: F_ D_ x_ quad F_ D_ x_ quad F_res D_res x_res &texta Die Spannkraft ist überall gleich F aber die Dehnungen x_i sind verschieden: &quad x_res x_ + x_Rightarrow fracFD_res fracFD_+fracFD_ Rightarrow fracD_res fracD_ + fracD_ Rightarrow D_res fracD_D_D_+D_ &textb Die Dehnungen sind gleich x aber die Spannkräfte F_i sind verschieden: &quad F_res F_ + F_Rightarrow D_resx D_x+D_x Rightarrow D_res D_+D_ &textc Dehnungen: x_res x_-x_ Spannkräfte: verschieden und entgegengesetzt gerichtet: &quad F_res F_ - F_Rightarrow D_resx D_x-D_-x Rightarrow D_res D_+D_ &textd Das ist eine Kombination von b und c also ist &quad D_res D_+D_+D_ * newpage
Meta Information
Exercise:
Einige Federn werden wie in Abbildung reffig:FedernKombinationena-d kombiniert. Bestimmen Sie welche Federkonstante eine einzelne Feder haben müsste welche die Kombination gleichwertig ersetzt. figureH includegraphicswidthtextwidth#image_path:FedernKombinationen# caption labelfig:FedernKombinationen figure
Solution:
% . September Lie. * &textFedergesetz: F_ D_ x_ quad F_ D_ x_ quad F_res D_res x_res &texta Die Spannkraft ist überall gleich F aber die Dehnungen x_i sind verschieden: &quad x_res x_ + x_Rightarrow fracFD_res fracFD_+fracFD_ Rightarrow fracD_res fracD_ + fracD_ Rightarrow D_res fracD_D_D_+D_ &textb Die Dehnungen sind gleich x aber die Spannkräfte F_i sind verschieden: &quad F_res F_ + F_Rightarrow D_resx D_x+D_x Rightarrow D_res D_+D_ &textc Dehnungen: x_res x_-x_ Spannkräfte: verschieden und entgegengesetzt gerichtet: &quad F_res F_ - F_Rightarrow D_resx D_x-D_-x Rightarrow D_res D_+D_ &textd Das ist eine Kombination von b und c also ist &quad D_res D_+D_+D_ * newpage
Einige Federn werden wie in Abbildung reffig:FedernKombinationena-d kombiniert. Bestimmen Sie welche Federkonstante eine einzelne Feder haben müsste welche die Kombination gleichwertig ersetzt. figureH includegraphicswidthtextwidth#image_path:FedernKombinationen# caption labelfig:FedernKombinationen figure
Solution:
% . September Lie. * &textFedergesetz: F_ D_ x_ quad F_ D_ x_ quad F_res D_res x_res &texta Die Spannkraft ist überall gleich F aber die Dehnungen x_i sind verschieden: &quad x_res x_ + x_Rightarrow fracFD_res fracFD_+fracFD_ Rightarrow fracD_res fracD_ + fracD_ Rightarrow D_res fracD_D_D_+D_ &textb Die Dehnungen sind gleich x aber die Spannkräfte F_i sind verschieden: &quad F_res F_ + F_Rightarrow D_resx D_x+D_x Rightarrow D_res D_+D_ &textc Dehnungen: x_res x_-x_ Spannkräfte: verschieden und entgegengesetzt gerichtet: &quad F_res F_ - F_Rightarrow D_resx D_x-D_-x Rightarrow D_res D_+D_ &textd Das ist eine Kombination von b und c also ist &quad D_res D_+D_+D_ * newpage
Contained in these collections:
-
Dynamik: Kraftgesetze by Lie
-
Federschaltungen by TeXercises

