Uran-235 im Kernkraftwerk Leibstadt
About points...
We associate a certain number of points with each exercise.
When you click an exercise into a collection, this number will be taken as points for the exercise, kind of "by default".
But once the exercise is on the collection, you can edit the number of points for the exercise in the collection independently, without any effect on "points by default" as represented by the number here.
That being said... How many "default points" should you associate with an exercise upon creation?
As with difficulty, there is no straight forward and generally accepted way.
But as a guideline, we tend to give as many points by default as there are mathematical steps to do in the exercise.
Again, very vague... But the number should kind of represent the "work" required.
When you click an exercise into a collection, this number will be taken as points for the exercise, kind of "by default".
But once the exercise is on the collection, you can edit the number of points for the exercise in the collection independently, without any effect on "points by default" as represented by the number here.
That being said... How many "default points" should you associate with an exercise upon creation?
As with difficulty, there is no straight forward and generally accepted way.
But as a guideline, we tend to give as many points by default as there are mathematical steps to do in the exercise.
Again, very vague... But the number should kind of represent the "work" required.
About difficulty...
We associate a certain difficulty with each exercise.
When you click an exercise into a collection, this number will be taken as difficulty for the exercise, kind of "by default".
But once the exercise is on the collection, you can edit its difficulty in the collection independently, without any effect on the "difficulty by default" here.
Why we use chess pieces? Well... we like chess, we like playing around with \(\LaTeX\)-fonts, we wanted symbols that need less space than six stars in a table-column... But in your layouts, you are of course free to indicate the difficulty of the exercise the way you want.
That being said... How "difficult" is an exercise? It depends on many factors, like what was being taught etc.
In physics exercises, we try to follow this pattern:
Level 1 - One formula (one you would find in a reference book) is enough to solve the exercise. Example exercise
Level 2 - Two formulas are needed, it's possible to compute an "in-between" solution, i.e. no algebraic equation needed. Example exercise
Level 3 - "Chain-computations" like on level 2, but 3+ calculations. Still, no equations, i.e. you are not forced to solve it in an algebraic manner. Example exercise
Level 4 - Exercise needs to be solved by algebraic equations, not possible to calculate numerical "in-between" results. Example exercise
Level 5 -
Level 6 -
When you click an exercise into a collection, this number will be taken as difficulty for the exercise, kind of "by default".
But once the exercise is on the collection, you can edit its difficulty in the collection independently, without any effect on the "difficulty by default" here.
Why we use chess pieces? Well... we like chess, we like playing around with \(\LaTeX\)-fonts, we wanted symbols that need less space than six stars in a table-column... But in your layouts, you are of course free to indicate the difficulty of the exercise the way you want.
That being said... How "difficult" is an exercise? It depends on many factors, like what was being taught etc.
In physics exercises, we try to follow this pattern:
Level 1 - One formula (one you would find in a reference book) is enough to solve the exercise. Example exercise
Level 2 - Two formulas are needed, it's possible to compute an "in-between" solution, i.e. no algebraic equation needed. Example exercise
Level 3 - "Chain-computations" like on level 2, but 3+ calculations. Still, no equations, i.e. you are not forced to solve it in an algebraic manner. Example exercise
Level 4 - Exercise needs to be solved by algebraic equations, not possible to calculate numerical "in-between" results. Example exercise
Level 5 -
Level 6 -
Question
Solution
Short
Video
\(\LaTeX\)


Wladyslaw Sojka, , 2021, digital photograph, Wikipedia
<Wikipedia> (retrieved on December 25, 2022)
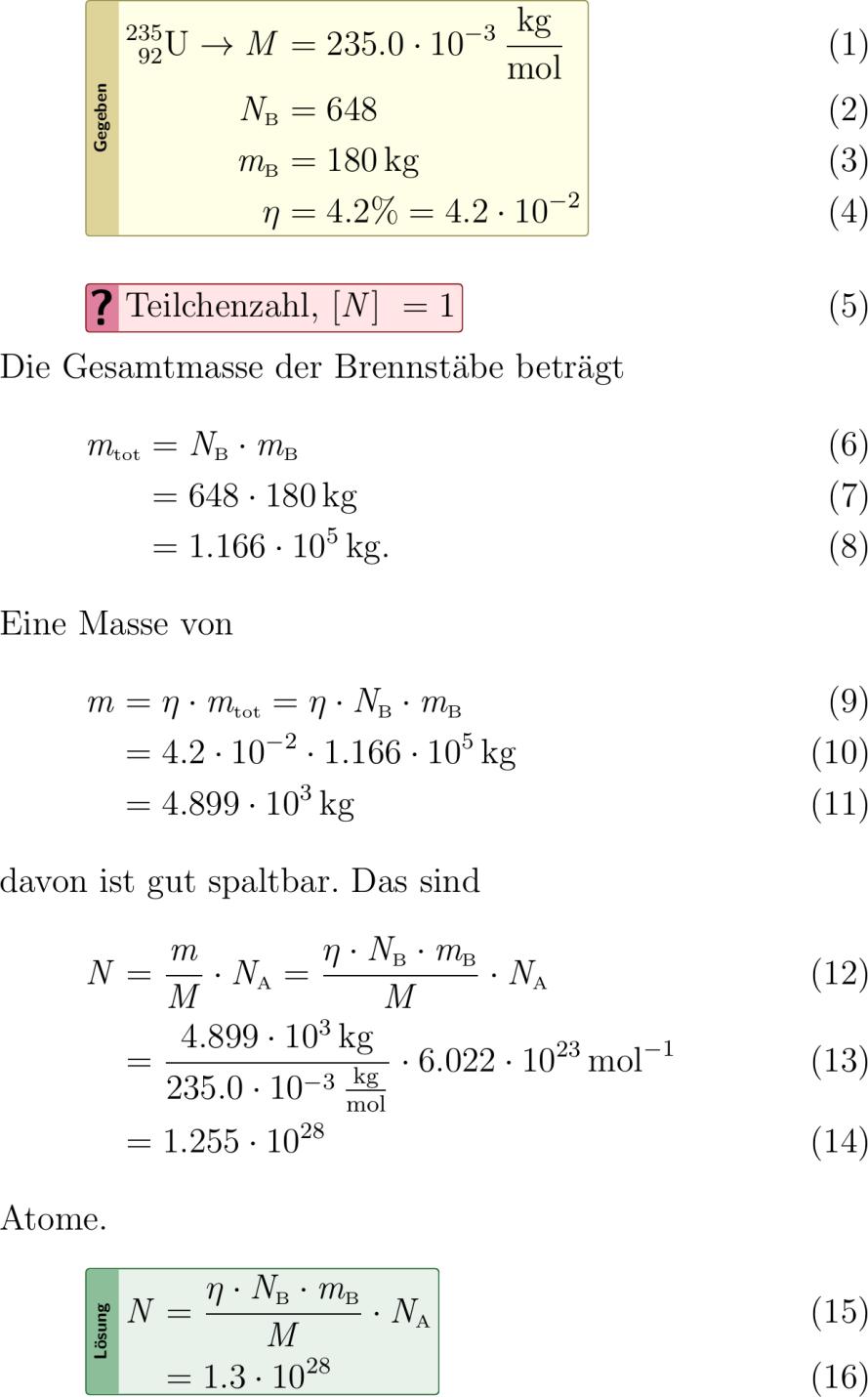
Exercise:
Wie viele isotopeU-Atome hat es in den Brennstäben des Kernkraftwerkes Leibstadt? Im Reaktorkern befinden sich Brennelemente mit je rund kg Uran. Allerdings sind nur .percent davon gut spaltbares Uran- der Rest ist Uran-.
Solution:
newqtyM.kilogrampermole newqtyNB newqtymBkg newqtyeto.percent newqtyet. newqtyper-modereciprocalNA.epermole % Geg isotopeU pf M M sscNB NB sscmB mB eta eto et % GesTeilchenzahlN % Die Gesamtmasse der Brennstäbe beträgt solqtymtsscNB sscmBNBn*mBnkg al sscmtot mtf NB mB mt. % Eine Masse von solqtymeta mtfetn*mtnkg al m eta sscmtot mf et mt m davon ist gut spaltbar. % Das sind solqtyNfracmfM sscNAmn/Mn*NAn al N fracmM sscNA Nf fracmM NA N Atome. % N Nf NII
Wie viele isotopeU-Atome hat es in den Brennstäben des Kernkraftwerkes Leibstadt? Im Reaktorkern befinden sich Brennelemente mit je rund kg Uran. Allerdings sind nur .percent davon gut spaltbares Uran- der Rest ist Uran-.
Solution:
newqtyM.kilogrampermole newqtyNB newqtymBkg newqtyeto.percent newqtyet. newqtyper-modereciprocalNA.epermole % Geg isotopeU pf M M sscNB NB sscmB mB eta eto et % GesTeilchenzahlN % Die Gesamtmasse der Brennstäbe beträgt solqtymtsscNB sscmBNBn*mBnkg al sscmtot mtf NB mB mt. % Eine Masse von solqtymeta mtfetn*mtnkg al m eta sscmtot mf et mt m davon ist gut spaltbar. % Das sind solqtyNfracmfM sscNAmn/Mn*NAn al N fracmM sscNA Nf fracmM NA N Atome. % N Nf NII
Meta Information
Exercise:
Wie viele isotopeU-Atome hat es in den Brennstäben des Kernkraftwerkes Leibstadt? Im Reaktorkern befinden sich Brennelemente mit je rund kg Uran. Allerdings sind nur .percent davon gut spaltbares Uran- der Rest ist Uran-.
Solution:
newqtyM.kilogrampermole newqtyNB newqtymBkg newqtyeto.percent newqtyet. newqtyper-modereciprocalNA.epermole % Geg isotopeU pf M M sscNB NB sscmB mB eta eto et % GesTeilchenzahlN % Die Gesamtmasse der Brennstäbe beträgt solqtymtsscNB sscmBNBn*mBnkg al sscmtot mtf NB mB mt. % Eine Masse von solqtymeta mtfetn*mtnkg al m eta sscmtot mf et mt m davon ist gut spaltbar. % Das sind solqtyNfracmfM sscNAmn/Mn*NAn al N fracmM sscNA Nf fracmM NA N Atome. % N Nf NII
Wie viele isotopeU-Atome hat es in den Brennstäben des Kernkraftwerkes Leibstadt? Im Reaktorkern befinden sich Brennelemente mit je rund kg Uran. Allerdings sind nur .percent davon gut spaltbares Uran- der Rest ist Uran-.
Solution:
newqtyM.kilogrampermole newqtyNB newqtymBkg newqtyeto.percent newqtyet. newqtyper-modereciprocalNA.epermole % Geg isotopeU pf M M sscNB NB sscmB mB eta eto et % GesTeilchenzahlN % Die Gesamtmasse der Brennstäbe beträgt solqtymtsscNB sscmBNBn*mBnkg al sscmtot mtf NB mB mt. % Eine Masse von solqtymeta mtfetn*mtnkg al m eta sscmtot mf et mt m davon ist gut spaltbar. % Das sind solqtyNfracmfM sscNAmn/Mn*NAn al N fracmM sscNA Nf fracmM NA N Atome. % N Nf NII
Contained in these collections:
-
Atomismus (Repetition) by uz
-
Atomismus by uz
-
Atomismus by pw
Asked Quantity:
Anzahl \(N\)
in
Anzahl \(\rm 1\)
Physical Quantity
Unit
Anzahl (\(\rm 1\))
Base?
SI?
Metric?
Coherent?
Imperial?
\(\rm1.59\cdot 10^{20}\,\): Enigma
\(\rm4.3\cdot 10^{19}\,\): Rubiks Cube
\(\rm18\cdot 10^{18}\,\): Schach-/Weizenkorn-Legende
\(\rm8.1\cdot 10^{67}\,\): 52er-Karten-Set
\(\rm1\cdot 10^{49}\,\): Atome der Erde

